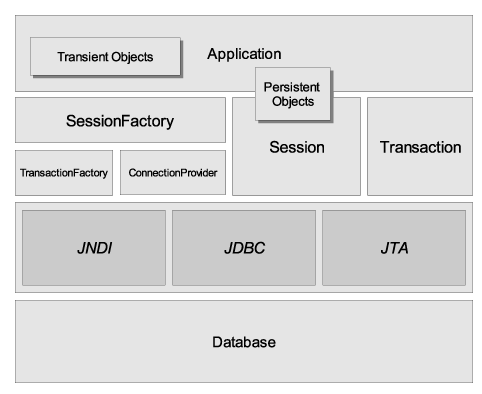
下面的图表提供了 Hibernate 体系结构的高层视图:
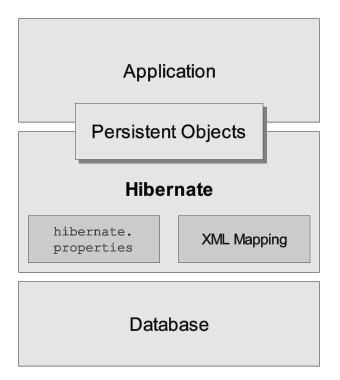
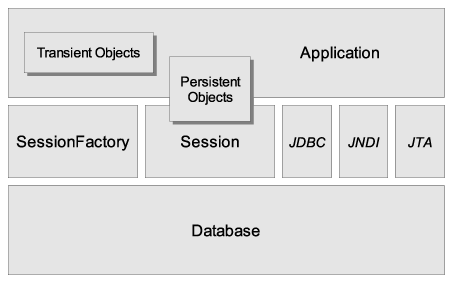
Unfortunately we cannot provide a detailed view of all possible runtime architectures. Hibernate is sufficiently flexible to be used in a number of ways in many, many architectures. We will, however, illustrate 2 specifically since they are extremes.
The "minimal" architecture has the application manage its own JDBC connections and provide those connections to Hibernate; additionally the application manages transactions for itself. This approach uses a minimal subset of Hibernate APIs.
Here are quick discussions about some of the API objects depicted in the preceding diagrams (you will see them again in more detail in later chapters).
- SessionFactory (
org.hibernate.SessionFactory) A thread-safe, immutable cache of compiled mappings for a single database. A factory for
org.hibernate.Sessioninstances. A client oforg.hibernate.connection.ConnectionProvider. Optionally maintains asecond level cacheof data that is reusable between transactions at a process or cluster level.- Session (
org.hibernate.Session) A single-threaded, short-lived object representing a conversation between the application and the persistent store. Wraps a JDBC
java.sql.Connection. Factory fororg.hibernate.Transaction. Maintains afirst level cacheof persistent the application's persistent objects and collections; this cache is used when navigating the object graph or looking up objects by identifier.- 持久的对象及其集合
Short-lived, single threaded objects containing persistent state and business function. These can be ordinary JavaBeans/POJOs. They are associated with exactly one
org.hibernate.Session. Once theorg.hibernate.Sessionis closed, they will be detached and free to use in any application layer (for example, directly as data transfer objects to and from presentation). 第 11 章 与对象共事 discusses transient, persistent and detached object states.- 瞬态(transient)和脱管(detached)的对象及其集合
Instances of persistent classes that are not currently associated with a
org.hibernate.Session. They may have been instantiated by the application and not yet persisted, or they may have been instantiated by a closedorg.hibernate.Session. 第 11 章 与对象共事 discusses transient, persistent and detached object states.- Transaction (
org.hibernate.Transaction) (Optional) A single-threaded, short-lived object used by the application to specify atomic units of work. It abstracts the application from the underlying JDBC, JTA or CORBA transaction. A
org.hibernate.Sessionmight span severalorg.hibernate.Transactions in some cases. However, transaction demarcation, either using the underlying API ororg.hibernate.Transaction, is never optional.- ConnectionProvider (
org.hibernate.connection.ConnectionProvider) (Optional) A factory for, and pool of, JDBC connections. It abstracts the application from underlying
javax.sql.DataSourceorjava.sql.DriverManager. It is not exposed to application, but it can be extended and/or implemented by the developer.- TransactionFactory (
org.hibernate.TransactionFactory) (Optional) A factory for
org.hibernate.Transactioninstances. It is not exposed to the application, but it can be extended and/or implemented by the developer.- Extension Interfaces
Hibernate 提供了很多可选的扩展接口,你可以通过实现它们来定制你的持久层的行为。具体请参考 API 文档。
JMX 是管理 Java 组件的 J2EE 标准。Hibernate 可以通过一个 JMX 标准服务来管理。在这个发行版本中,我们提供了一个 MBean 接口的实现,即 org.hibernate.jmx.HibernateService。
Another feature available as a JMX service is runtime Hibernate statistics. See 第 3.4.6 节 “Hibernate 的统计(statistics)机制” for more information.
使用 Hibernate 的大多数应用程序需要某种形式的“上下文相关的”会话,特定的会话在整个特定的上下文范围内始终有效。然而,对不同类型的应用程序而言,要为什么是组成这种“上下文”下一个定义通常是困难的;不同的上下文对“当前”这个概念定义了不同的范围。在 3.0 版本之前,使用 Hibernate 的程序要么采用自行编写的基于 ThreadLocal 的上下文会话,要么采用 HibernateUtil 这样的辅助类,要么采用第三方框架(比如 Spring 或 Pico),它们提供了基于代理(proxy)或者基于拦截器(interception)的上下文相关的会话。
从 3.0.1 版本开始,Hibernate 增加了 SessionFactory.getCurrentSession() 方法。一开始,它假定了采用 JTA 事务,JTA 事务定义了当前 session 的范围和上下文(scope 和 context)。因为有好几个独立的 JTA TransactionManager 实现稳定可用,不论是否被部署到一个 J2EE 容器中,大多数(假若不是所有的)应用程序都应该采用 JTA 事务管理。基于这一点,采用 JTA 的上下文相关的会话可以满足你一切需要。
更好的是,从 3.1 开始,SessionFactory.getCurrentSession() 的后台实现是可拔插的。因此,我们引入了新的扩展接口(org.hibernate.context.CurrentSessionContext)和新的配置参数(hibernate.current_session_context_class),以便对什么是当前会话的范围(scope)和上下文(context)的定义进行拔插。
请参阅 org.hibernate.context.CurrentSessionContext 接口的 Javadoc,那里有关于它的契约的详细讨论。它定义了单一的方法,currentSession(),特定的实现用它来负责跟踪当前的上下文相关的会话。Hibernate 内置了此接口的三种实现:
org.hibernate.context.JTASessionContext:当前会话根据JTA来跟踪和界定。这和以前的仅支持 JTA 的方法是完全一样的。详情请参阅 Javadoc。org.hibernate.context.ThreadLocalSessionContext:当前会话通过当前执行的线程来跟踪和界定。详情也请参阅 Javadoc。org.hibernate.context.ManagedSessionContext:当前会话通过当前执行的线程来跟踪和界定。但是,你需要负责使用这个类的静态方法将Session实例绑定、或者取消绑定,它并不会打开(open)、flush 或者关闭(close)任何Session。
The first two implementations provide a "one session - one database transaction" programming model. This is also known and used as session-per-request. The beginning and end of a Hibernate session is defined by the duration of a database transaction. If you use programmatic transaction demarcation in plain JSE without JTA, you are advised to use the Hibernate Transaction API to hide the underlying transaction system from your code. If you use JTA, you can utilize the JTA interfaces to demarcate transactions. If you execute in an EJB container that supports CMT, transaction boundaries are defined declaratively and you do not need any transaction or session demarcation operations in your code. Refer to 第 13 章 事务和并发 for more information and code examples.
hibernate.current_session_context_class 配置参数定义了应该采用哪个 org.hibernate.context.CurrentSessionContext 实现。注意,为了向下兼容,如果未配置此参数,但是存在 org.hibernate.transaction.TransactionManagerLookup 的配置,Hibernate 会采用org.hibernate.context.JTASessionContext。一般而言,此参数的值指明了要使用的实现类的全名,但那三种内置的实现可以使用简写,即 "jta"、"thread" 和 "managed"。